Unlocking the Power of Control Relay Coil Symbols
Ever wondered about those squiggly lines on electrical diagrams? They're not just random doodles. They represent the heart of many electrical control systems: the control relay coil. Understanding this fundamental symbol is crucial for anyone working with electrical circuits, from hobbyists to seasoned engineers. Let's unravel the mysteries of this essential component and empower you to effectively utilize its capabilities.
Control relays are the unsung heroes of automation, silently orchestrating complex processes in countless applications. A control relay coil symbol, in essence, represents the electromagnet that activates the relay. By energizing this coil, we control the switching action of the relay contacts, enabling us to manage high-power circuits with low-power signals. This seemingly simple function forms the foundation of sophisticated control systems in industrial automation, home appliances, and even spacecraft.
The concept of using electromagnetism for remote switching dates back to the early 19th century, with the invention of the telegraph. The development of the control relay, and its symbolic representation, evolved from these early experiments, driven by the need for reliable and efficient switching mechanisms. The standardization of relay symbols allowed engineers to communicate complex circuit designs clearly and concisely, fostering collaboration and innovation.
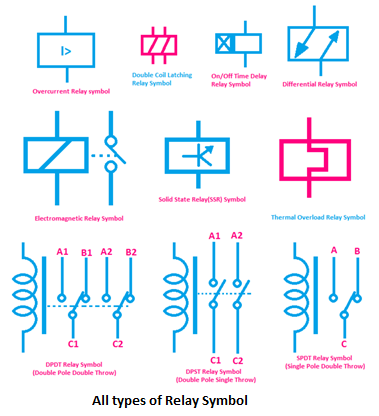
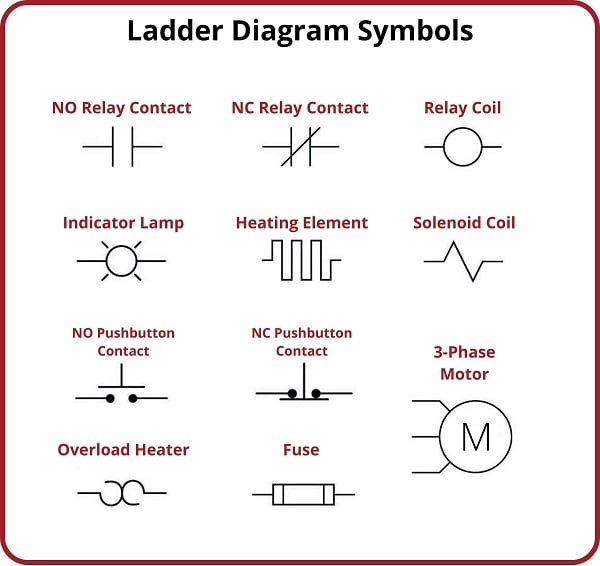
The control relay coil symbol, typically a circle with a connected line representing the coil winding, signifies the activating element of the relay. Understanding this symbol is essential for interpreting electrical diagrams and troubleshooting control circuits. Misinterpreting this symbol can lead to incorrect wiring, malfunctioning systems, and even safety hazards. Therefore, a clear grasp of its meaning is paramount for anyone involved in electrical design or maintenance.
Relay coil symbols are further refined with additional markings to indicate specific coil characteristics, such as operating voltage (AC or DC) and coil resistance. This detailed representation facilitates accurate circuit analysis and component selection. For instance, a symbol with a straight line through it indicates a DC coil, while a symbol with a sinusoidal wave indicates an AC coil. This precise visual language ensures clarity and prevents ambiguity in complex electrical systems.
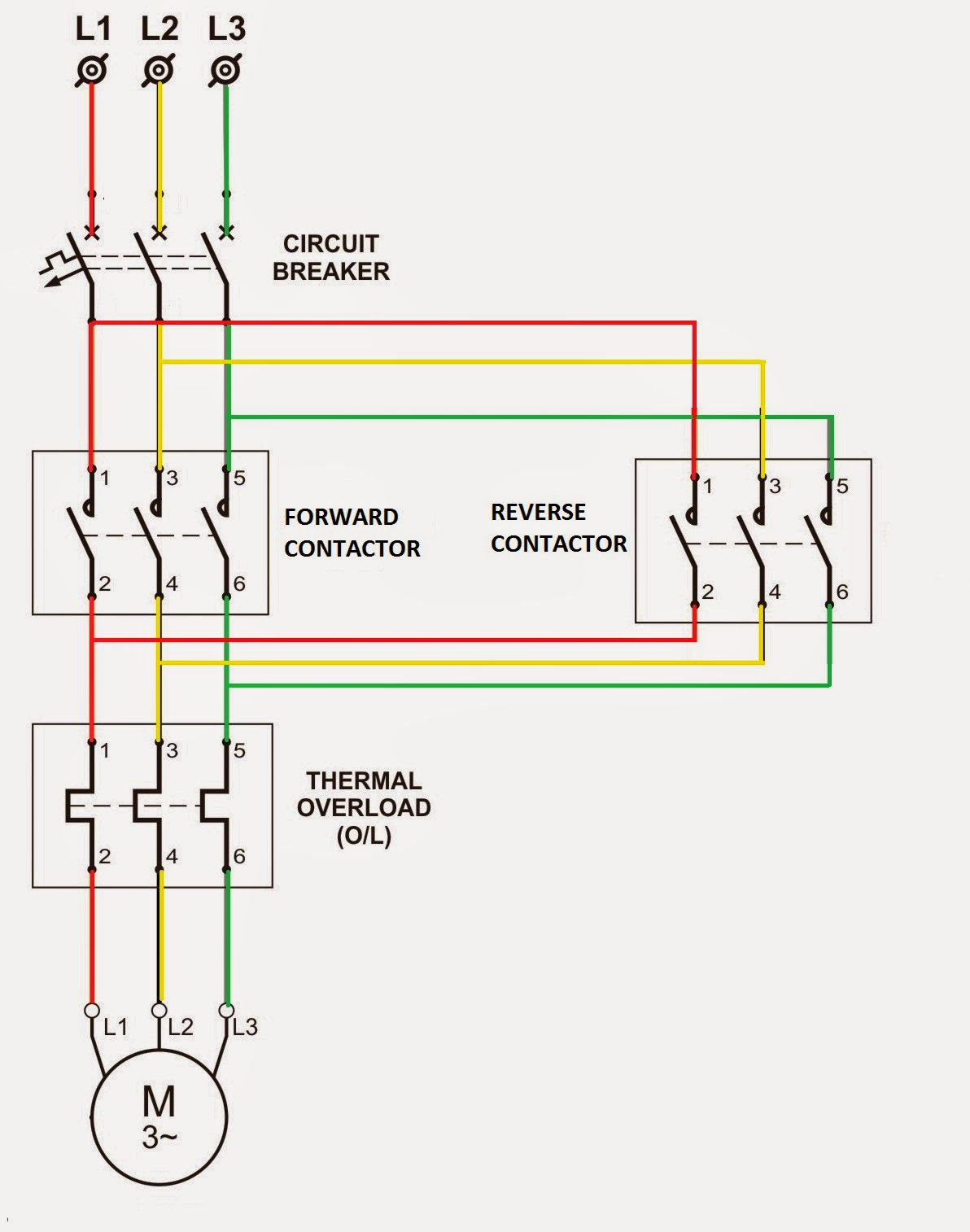
One key benefit of using relays is isolation. The control signal and the controlled circuit are electrically separated, protecting sensitive control circuitry from high voltages and currents. Another advantage is amplification. A small current through the relay coil can switch a much larger current through the relay contacts. Finally, relays enable complex logic functions, allowing for automation and control based on various input conditions.
If you're troubleshooting a relay circuit, start by checking the coil voltage. Is it receiving the correct voltage? Next, inspect the coil for continuity. A broken coil will prevent the relay from activating. Finally, examine the relay contacts for wear and tear. Damaged contacts can hinder proper switching action.
Common issues with relay coils include overheating due to excessive current, open circuits due to broken windings, and short circuits within the coil. Solutions involve using appropriate fuses, ensuring proper voltage levels, and replacing faulty relays.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Relays
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Electrical Isolation | Slower Switching Speed than Solid-State Devices |
| Amplification | Mechanical Wear and Tear |
| Logic Functions | Can Generate Audible Clicks |
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is a relay coil? - The electromagnetic component that activates the relay.
2. What does the control relay coil symbol represent? - The electromagnet within the relay.
3. Why is understanding the symbol important? - For proper circuit interpretation and troubleshooting.
4. How do AC and DC coil symbols differ? - AC symbols typically feature a sinusoidal wave, while DC symbols have a straight line.
5. What are common problems with relay coils? - Overheating, open circuits, and short circuits.
6. How can I troubleshoot a relay coil? - Check coil voltage, continuity, and contact condition.
7. What are the benefits of using relays? - Isolation, amplification, and logic functions.
8. What are the disadvantages of using relays? - Slower switching speed, mechanical wear, and audible clicks.
Tips and tricks for working with relays include using appropriate suppression diodes across the coil to prevent voltage spikes, choosing the correct relay for the application's voltage and current requirements, and ensuring proper ventilation to prevent overheating.
In conclusion, the control relay coil symbol represents a fundamental building block of electrical control systems. Understanding its significance is paramount for anyone working with electrical circuits. From its historical roots in the telegraph to its modern applications in sophisticated automation, the relay remains a critical component in countless devices and systems. By grasping the principles behind this symbol, and utilizing the troubleshooting tips and best practices discussed, you can effectively harness the power of relays to create reliable, efficient, and innovative electrical systems. Take the time to truly understand the control relay coil symbol and unlock a world of possibilities in electrical design and control.
Unlocking spanish fluency fourth grade worksheets and beyond
Sage green paint uk a timeless hue for modern homes
Top rated a1 carpet cleaning services near you