Decoding the Federal GS Pay Scale: Steps to Understanding Your Salary
Ever wondered how federal government salaries are determined? It's not arbitrary. The General Schedule (GS) pay scale, a structured system with its own unique set of rules, governs the compensation for most federal employees. Understanding the nuances of this system, particularly the within-grade increases, commonly referred to as "steps," is crucial for navigating your career within the federal government.
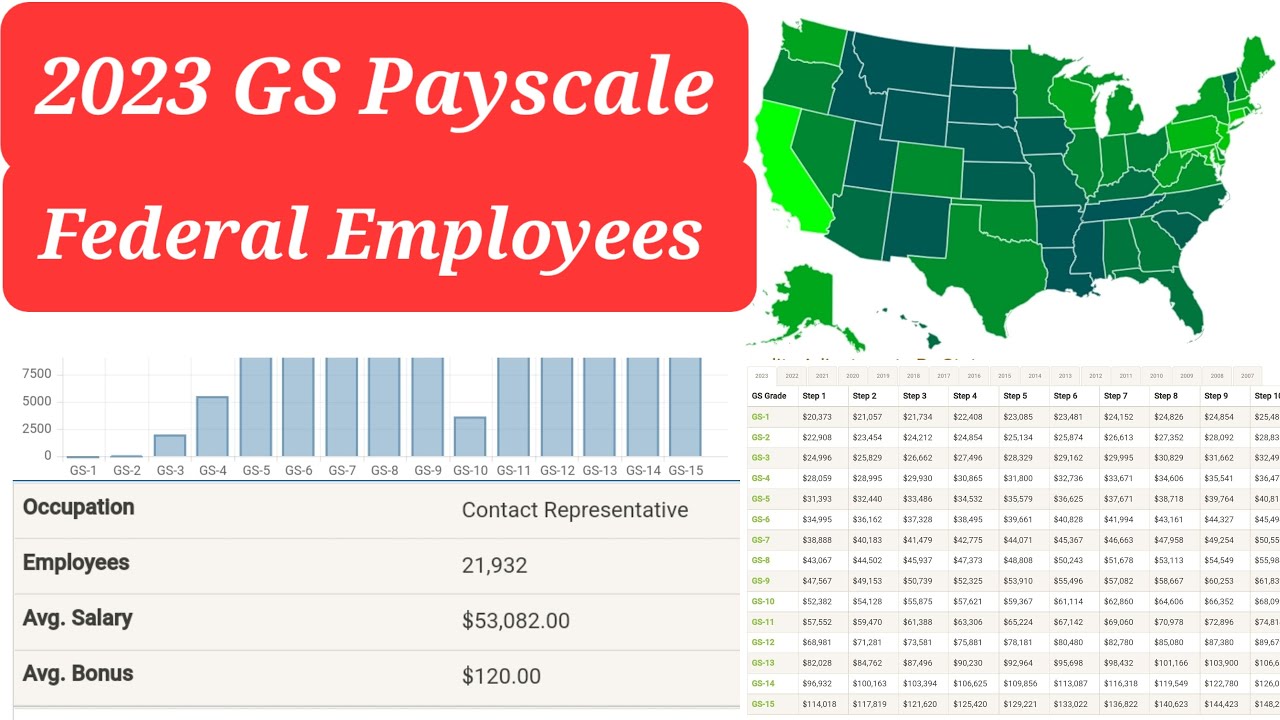
The GS pay scale isn't just a list of numbers; it's a roadmap to your potential earnings. Each GS grade, from GS-1 to GS-15, represents a different level of responsibility and complexity. Within each grade are ten steps, representing incremental salary increases based on time in service and performance. These federal GS pay scale step increases are not automatic; they're earned. Mastering how this system functions can significantly impact your long-term financial well-being.
Navigating the federal GS pay scale steps requires understanding several key components. Locality pay, a critical element, adjusts base salaries based on the cost of living in different geographic areas. This means a GS-9, Step 5 employee in San Francisco will earn a different salary than a GS-9, Step 5 employee in Kansas City. Another critical aspect is understanding how promotions impact your placement on the GS pay scale. Moving up the GS ladder isn't just about a new title; it's about leveraging your experience and qualifications to land at a higher step within your new grade.
Beyond the basic mechanics, understanding the history and rationale behind the GS pay system can offer valuable context. The system, established in the Classification Act of 1923, aimed to create a standardized and transparent method for compensating federal employees based on the principle of equal pay for equal work. This structure, while refined over the decades, continues to be the cornerstone of federal compensation. However, debates around pay equity, particularly relating to locality pay adjustments and compression between grades, remain ongoing.
To truly grasp the intricacies of the GS system, you need to go beyond surface-level understanding. Deciphering the interplay of grade, step, and locality pay can feel like solving a complex equation. But armed with the right knowledge, you can unlock the potential of the GS pay scale and chart a clear path toward financial growth within your federal career.
One key benefit of the structured GS pay scale steps is predictability. Employees can anticipate their salary progression based on their time in grade. Another advantage is transparency. The pay tables are publicly available, allowing employees to clearly see the potential earnings at each grade and step. This transparency fosters a sense of fairness and equity within the system.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the GS Pay Scale
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Predictable salary progression | Potential salary compression at higher grades |
| Transparency and fairness | Limited flexibility for rewarding exceptional performance outside of step increases |
| Standardized system across federal agencies | Locality pay adjustments can create disparities between regions |
Best Practices:
1. Research Locality Pay: Understand how your location impacts your salary.
2. Negotiate Your Starting Step: When accepting a federal position, you can often negotiate your initial step placement based on your experience.
3. Track Your Step Increases: Be aware of your time-in-grade requirements for step increases.
4. Understand Promotion Rules: Learn how promotions affect your placement on the new grade's pay scale.
5. Explore Additional Compensation: Be aware of potential bonuses, awards, and other incentives available within your agency.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. How often do step increases occur? (Answer: Generally annually or every two years, depending on the step.)
2. What is a within-grade increase? (Answer: A step increase within the same GS grade.)
3. How is locality pay calculated? (Answer: Based on surveys of local salary rates.)
4. Can I negotiate my salary when promoted? (Answer: You can often negotiate your step placement on the new grade.)
5. How do I find the current GS pay tables? (Answer: The Office of Personnel Management (OPM) website.)
6. What are special rate tables? (Answer: Pay tables for certain occupations or geographic areas with unique pay needs.)
7. How does performance affect my step increases? (Answer: Generally, satisfactory performance is required.)
8. What is a "step promotion?" (Answer: This is often when you are promoted to the next higher grade and your step remains the same numerically, resulting in a larger salary increase.)
Tips and Tricks: Utilize online GS pay calculators to estimate your salary. Consult with your agency's HR department for specific guidance on pay and promotion policies.
The federal GS pay scale, with its intricate system of grades and steps, can initially appear daunting. However, understanding its complexities is essential for managing your career and maximizing your earning potential within the federal government. By understanding the rules governing federal GS pay scale steps, including locality pay adjustments and promotion implications, you can strategically navigate your career progression and ensure you are appropriately compensated for your contributions. Take the time to research, ask questions, and plan accordingly. Your future financial well-being within the federal system depends on it. By proactively managing your understanding of the GS pay scale, you empower yourself to take control of your career trajectory and ensure you are rewarded fairly for your hard work and dedication. Engage with your agency's human resources department, utilize available resources, and stay informed about changes to the GS system. Your future self will thank you.
Decoding behrs peppery the spice your walls need
Decoding the enigma of omar algo anda mal lyrics
Mastering boat entry a safe and smooth embarkation